CommonGen
A Constrained Text Generation Challengefor Generative Commonsense Reasoning
Bill Yuchen Lin, Wangchunshu Zhou, Ming Shen, Pei Zhou, Chandra Bhagavatula, Yejin Choi, Xiang Ren



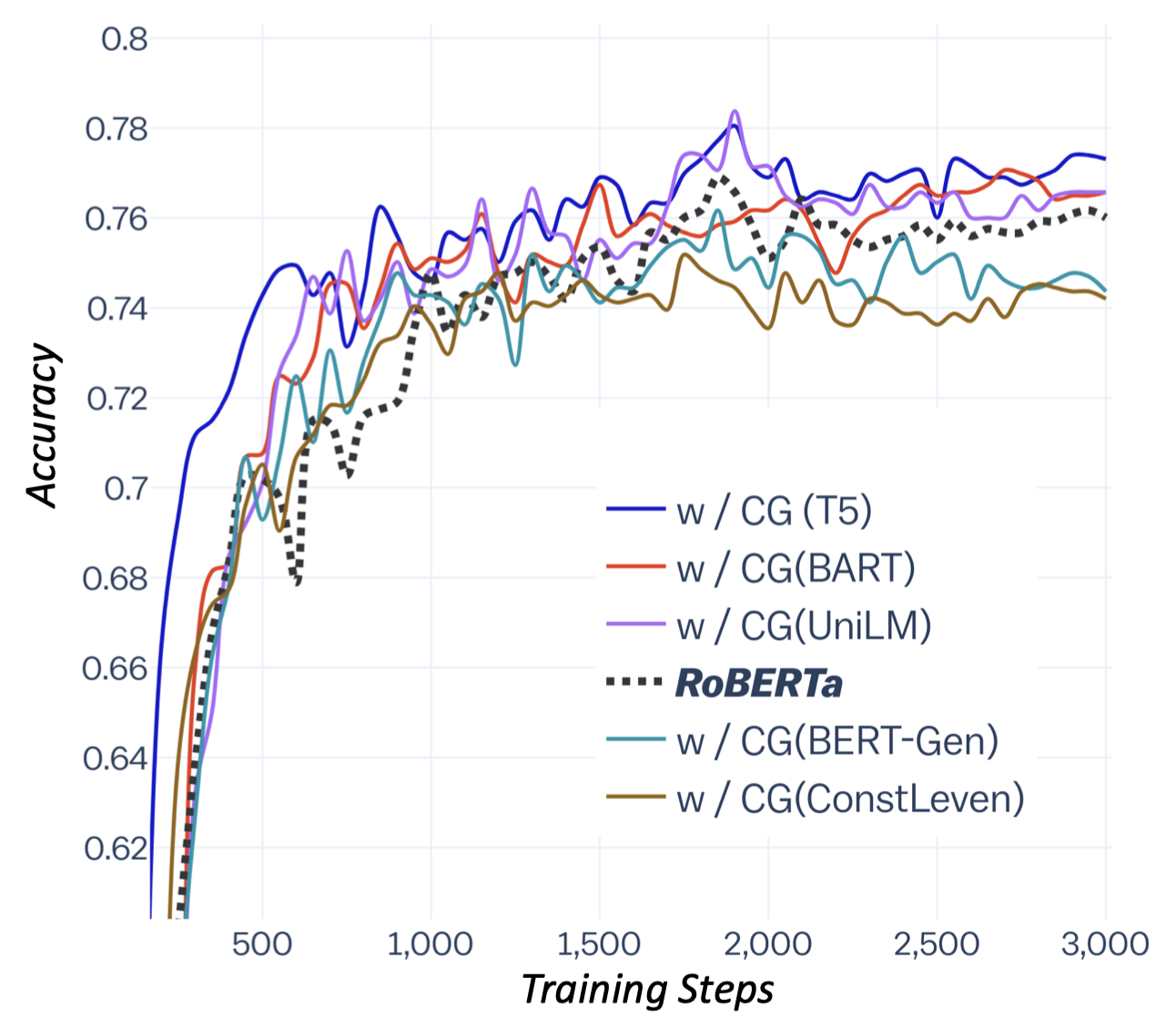
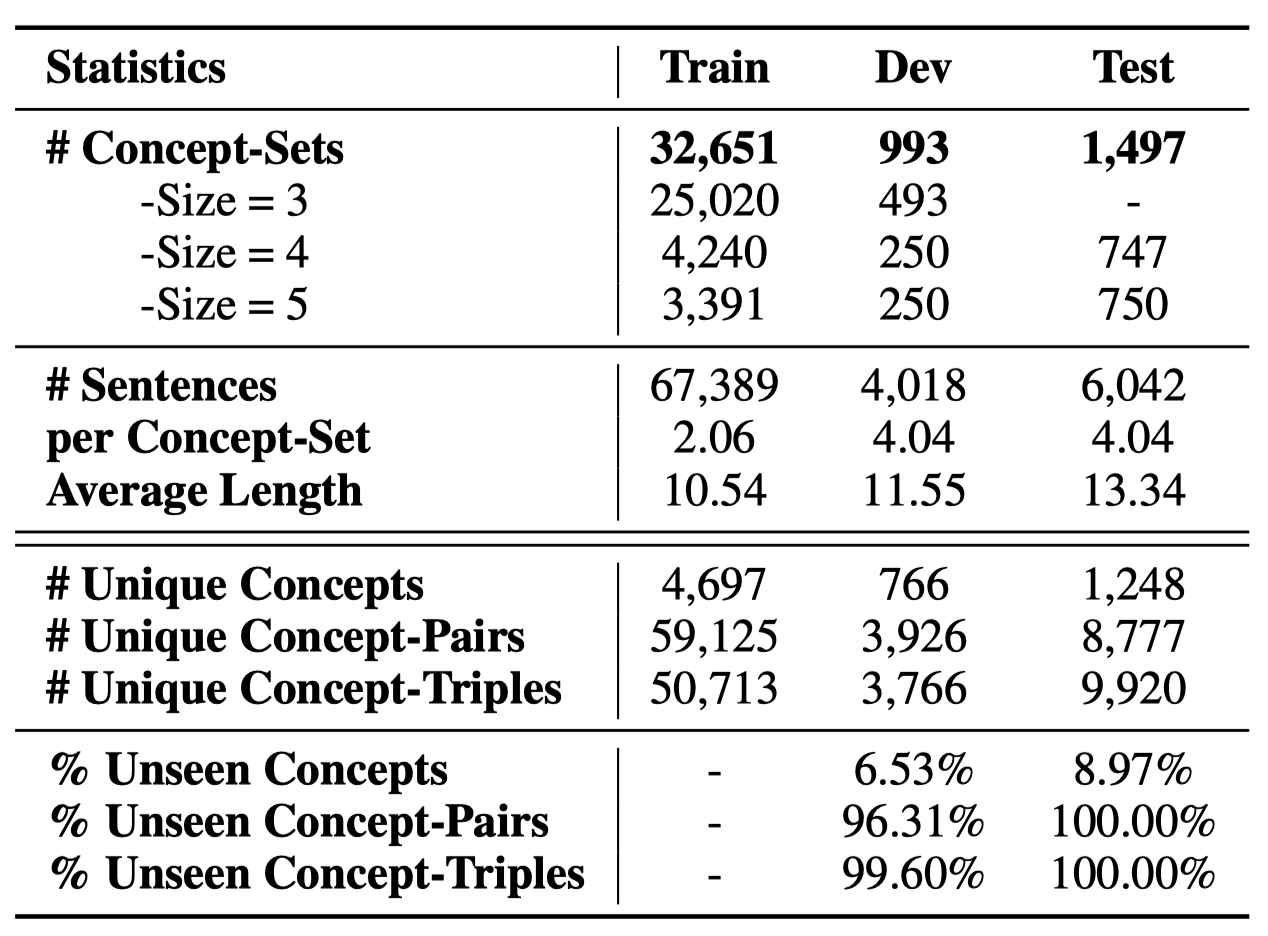
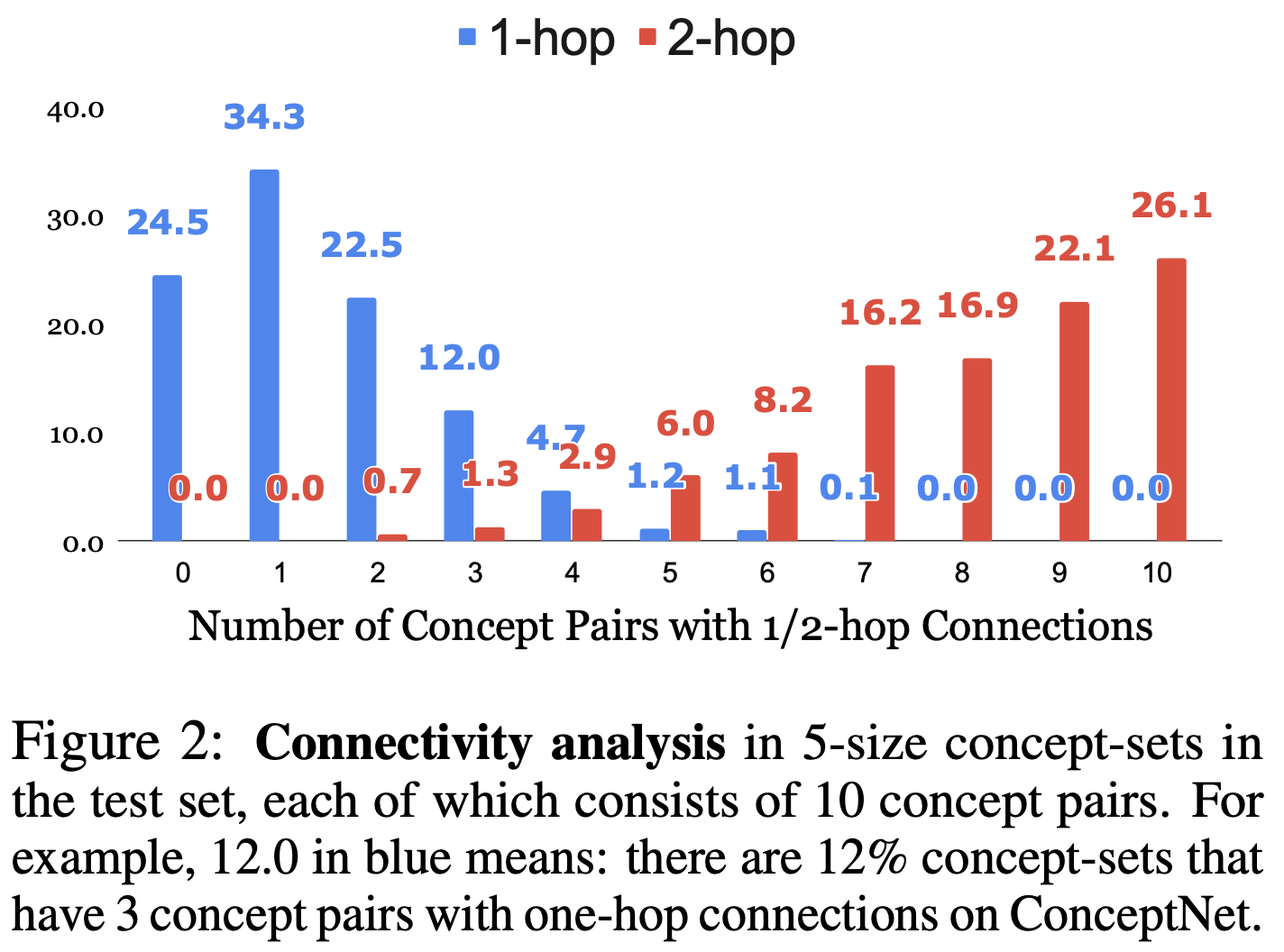
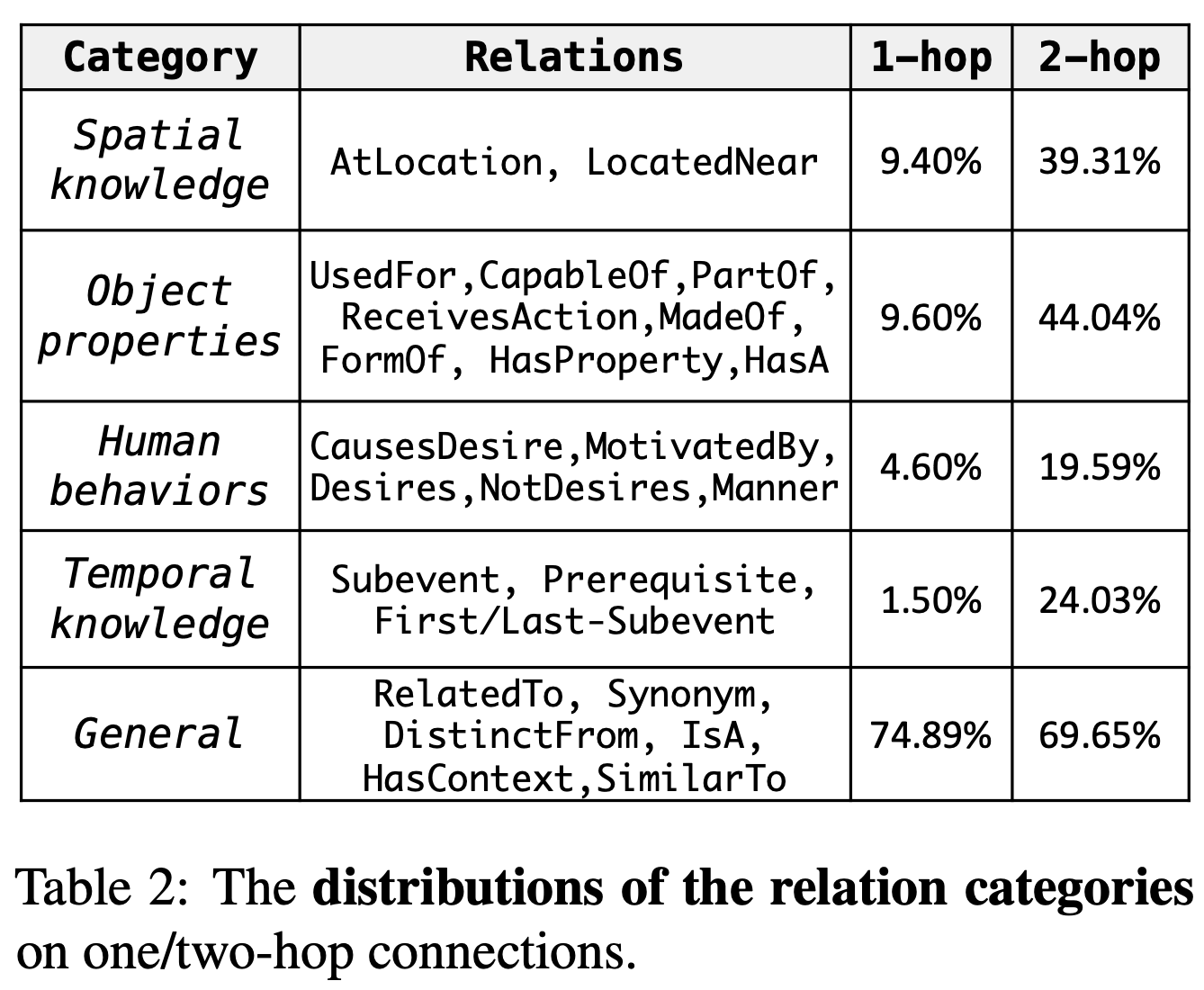
We use the AMT platform for collecting such sentences for covered the top-ranked 2,500 concept-sets in the sampled results from large visual caption copora. Each of them is assigned to at least three different workers. Furthermore, we use the remaining concept-sets as the training examples, for which we use the associated captions as the target outputs. There are on average 4 sentences for each example in dev and test sets, which provide a more diverse test-bed for further automatic and manual evaluation. We highlight the ratio of novel concept compositions (i.e., concept, concept-pair, and concept-triple) in dev/test, which never (co-)occur in training examples. This makes CommonGen challenging in terms of compositional generalization ability.
@inproceedings{lin-etal-2020-commongen,
title = "{C}ommon{G}en: A Constrained Text Generation Challenge for Generative Commonsense Reasoning",
author = "Lin, Bill Yuchen and
Zhou, Wangchunshu and
Shen, Ming and
Zhou, Pei and
Bhagavatula, Chandra and
Choi, Yejin and
Ren, Xiang",
booktitle = "Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020",
month = nov,
year = "2020",
address = "Online",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.findings-emnlp.165",
pages = "1823--1840",
}